Combine with code
The Decentraland Editor plus custom code is a very powerful combination for creating content. You can use the Visual Editor to position items intuitively, and then write code that interacts with these items with complete freedom. You can even place a smart item, that has its own default behavior, and write code that reacts to when the item is activated.
For example, you can take advantage of an existing lever smart item, that already comes with its sounds and animations and states, and write code that detects when the lever is pulled to run your own custom logic.
Export to desktop #
To edit the code in a scene created with the web editor , you must export the scene to the Desktop Editor.
📔 Note: If you don’t have the Desktop Editor installed, follow the steps in the following page before your start.
- Click the Download icon on the top menu while editing the scene.

- This will download a .zip file, extract it.
- Open the extracted folder with Visual Studio Code. The folder must be open at the root of the project.
Once you’re done, you can edit the files under the /src folder to add behavior with code to your scene. You can also open the Visual Editor to keep editing items visually, just like in the web editor.
Reference an item #
When using the Decentraland Editor and adding entities via the drag-and-drop Visual Editor, each entity has a unique name. Use the engine.getEntityOrNullByName() function to reference one of these entities from your code. Pass the entity’s name as a string, as written on the Visual Editor’s UI, in the tree view on the left.
function main() {
const door = engine.getEntityOrNullByName('Pot1')
}
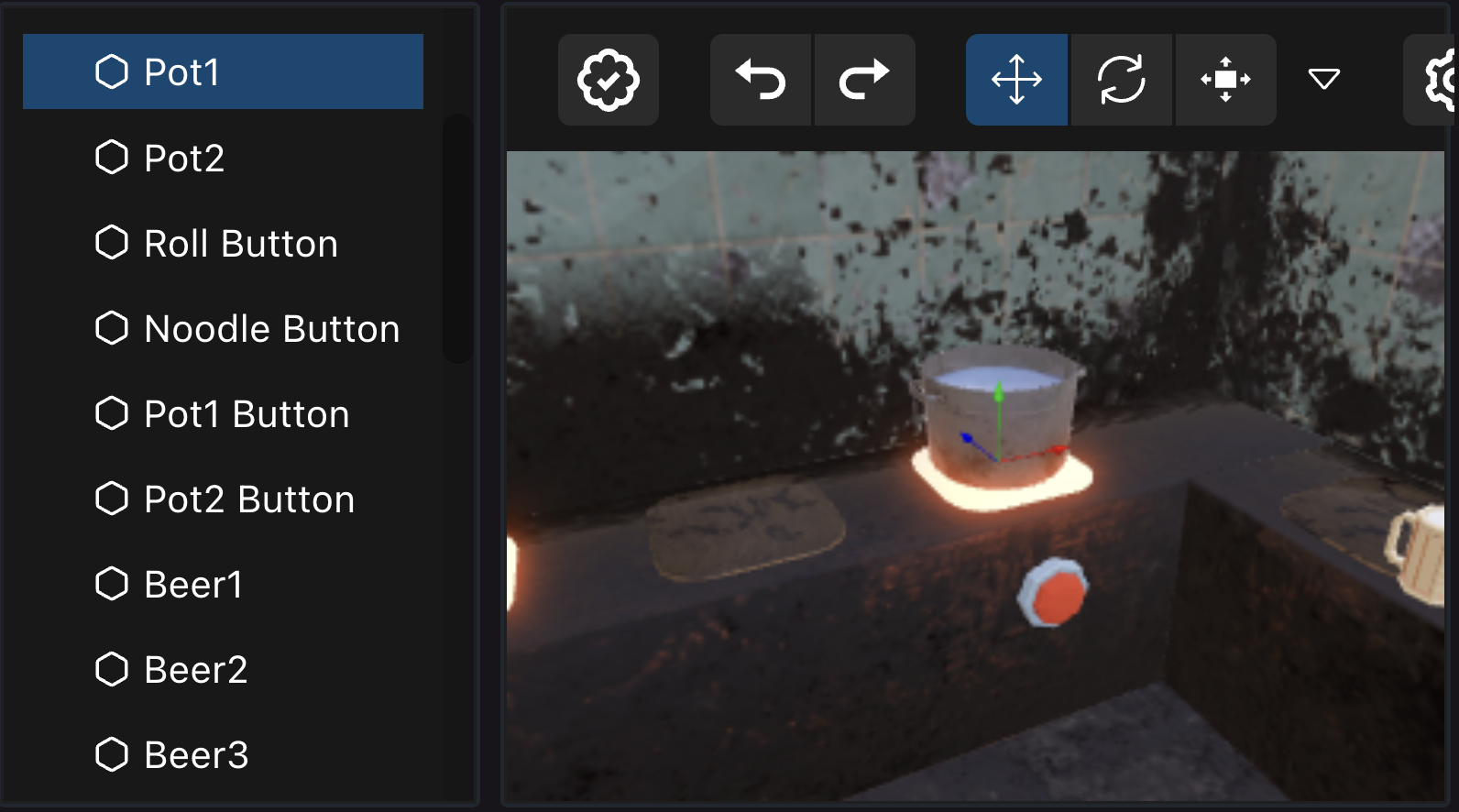
📔 Note: Make sure you only useengine.getEntityOrNullByName()inside themain()function, in functions that run aftermain(), or in a system. If used outside one of those contexts, the entities created in the Visual Editor may not yet be instanced.
You’re free to perform any action on an entity fetched via this method, like add or remove components, modify values of existing components, or remove the entity from the engine.
function main() {
// fetch entity
const door = engine.getEntityOrNullByName('door-3')
// verify that the entity exists
if (door) {
// add a pointer events callback
pointerEventsSystem.onPointerDown(
{
entity: door,
opts: { button: InputAction.IA_PRIMARY, hoverText: 'Open' },
},
function () {
// open door
}
)
}
}
All the entities added via the Visual Editor have a Name component, you can also iterate over all of them like this:
function main() {
for (const [entity, name] of engine.getEntitiesWith(Name)) {
console.log({ entity, name })
}
}
Smart item triggers #
You can detect a smart item’s Trigger events, and respond to these with custom code. For example, you could place a button smart item, and activate custom code when the button is clicked.
Use getTriggerEvents to fetch an object that can handle trigger events on from a particular smart item, then use the .on() function of the returned object to subscribe a callback function. This callback function gets executed every time that the trigger event happens.
For example, if a scene has a button with the following generic On Click event, you can write the code below to run custom code whenever the button is activated.
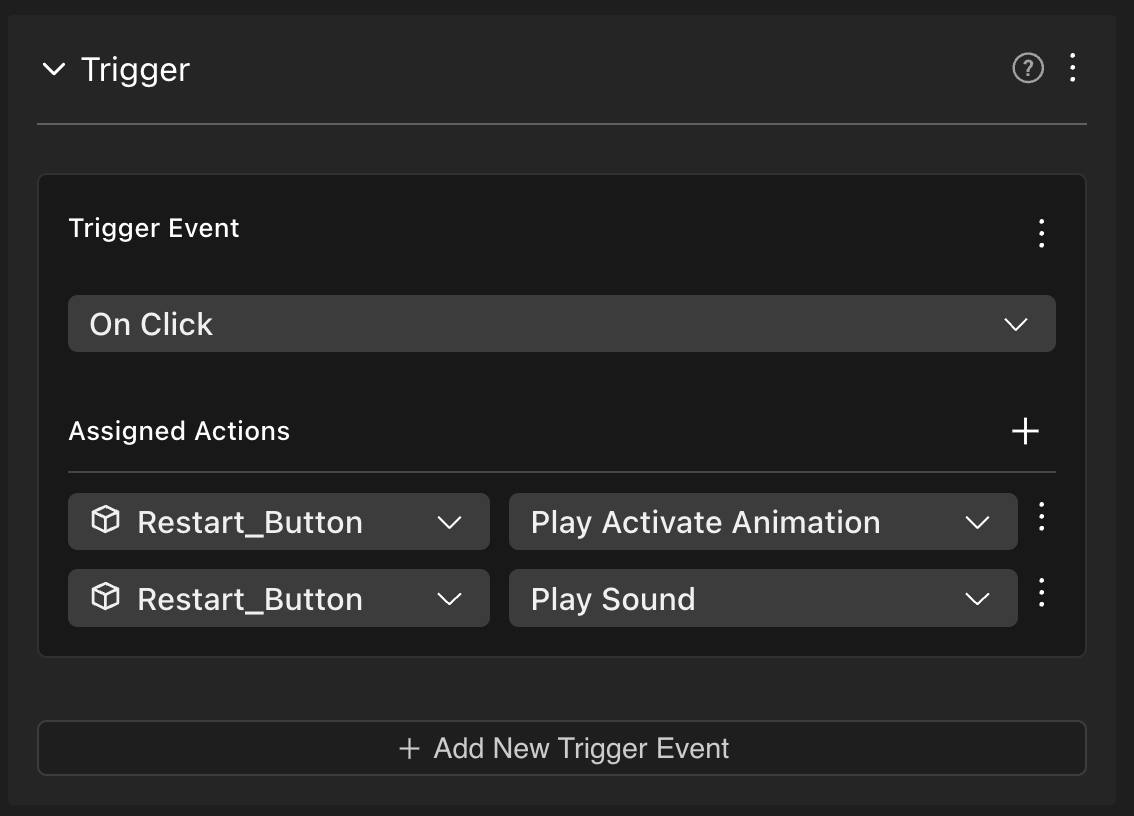
import { getTriggerEvents, getActionEvents } from '@dcl/asset-packs/dist/events'
import { TriggerType } from '@dcl/asset-packs'
function main() {
const restart = engine.getEntityOrNullByName('Restart_Button')
if (restart) {
const restart_event = getTriggerEvents(restart)
restart_event.on(TriggerType.ON_CLICK, () => {
// restartGame()
})
}
}
You can similarly subscribe to any other type of trigger events, like ON_PLAYER_ENTERS_AREA, ON_SPAWN, ON_TWEEN_END, etc.
Smart item actions #
You can detect the activation of a smart item’s Actions, and respond to these with custom code. For example, you could place a door smart item, and run custom code whenever the Open action gets called.
Use getActionEvents to fetch an object for handling the actions of a specific smart item. Then you can use the .on() function of the returned object to subscribe a callback function. This callback function gets executed every time that the action happens, regardless of if the action was activated by another smart item, or even by custom code of your own.
For example, if a scene has a door with the following generic Open action, you can write the code below to run custom code whenever the door is opened.
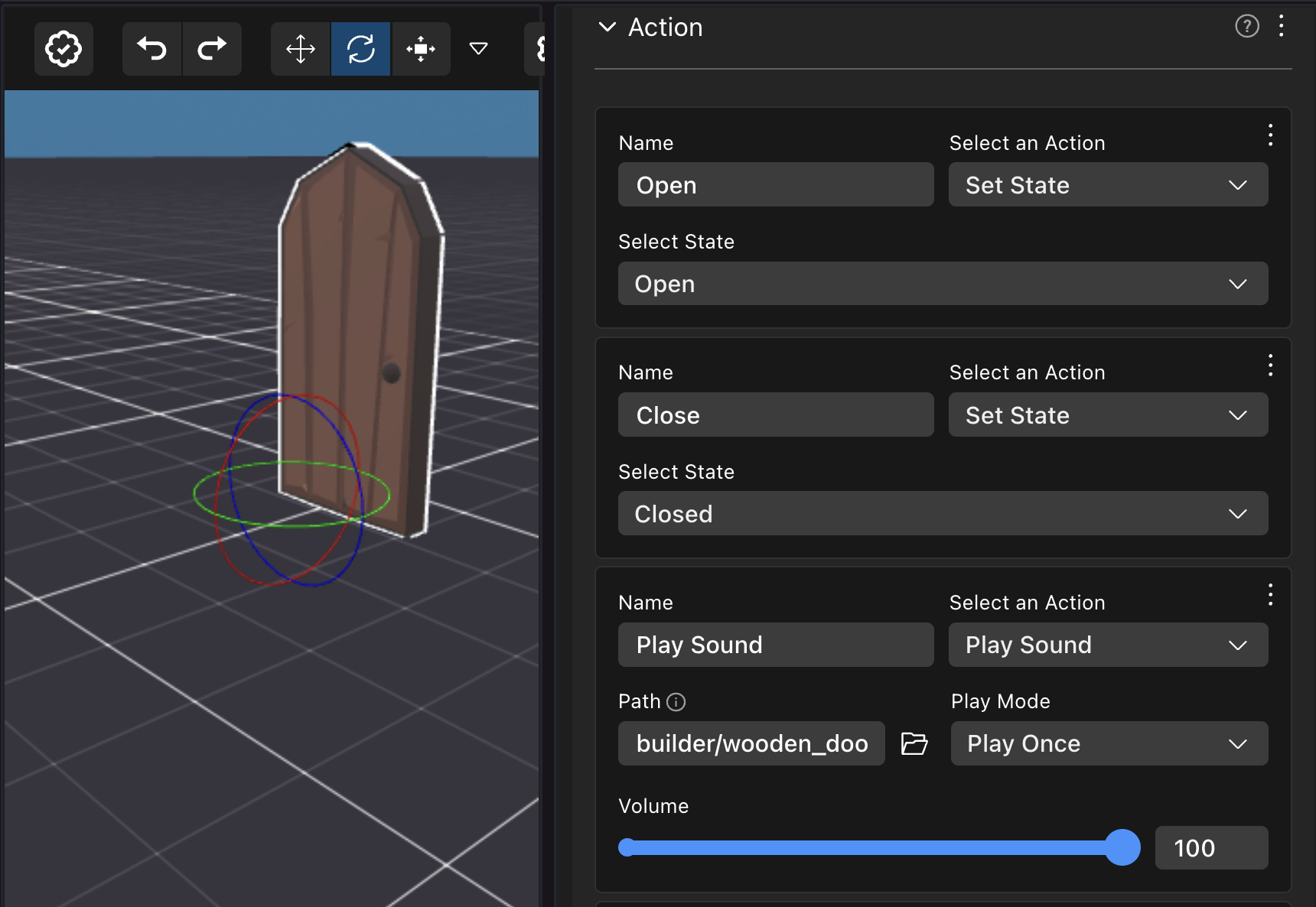
import { getTriggerEvents, getActionEvents } from '@dcl/asset-packs/dist/events'
function main() {
const door = engine.getEntityOrNullByName('Wooden Door')
if (door) {
// detect actions
const actions = getActionEvents(door)
actions.on('Open', () => {
console.log("Door opened!!")
// custom code
})
// detect triggers
const triggers = getTriggerEvents(door)
triggers.on(TriggerType.ON_CLICK, () => {
console.log("Door clicked!!")
// custom code
})
}
}
💡 Tip: If you’re not trying to do something very complicated, instead of writing code you can also create a custom smart item to handle the actions you want to perform. See Making any item smart